Spring Boot 集成MyBatis
一、前言
一个现实的场景是:当我们开发一个Web工程时,架构师和开发工程师可能更关心项目技术结构上的设计。而几乎所有结构良好的软件(项目)都使用了分层设计。分层设计是将项目按技术职能分为几个内聚的部分,从而将技术或接口的实现细节隐藏起来。

从另一个角度上来看,结构上的分层往往也能促进了技术人员的分工,可以使开发人员更专注于某一层业务与功能的实现,比如前端工程师只关心页面的展示与交互效果(例如专注于HTML,JS等),而后端工程师只关心数据和业务逻辑的处理(专注于Java,Mysql等)。两者之间通过标准接口(协议)进行沟通。
在实现分层的过程中我们会使用一些框架,例如SpringMVC。但利用框架带来了一些使用方面的问题。我们经常要做的工作就是配置各种XML文件,然后还需要搭建配置Tomcat或者Jetty作为容器来运行这个工程。每次构建一个新项目,都要经历这个流程。更为不幸的是有时候前端人员为了能在本地调试或测试程序,也需要先配置这些环境,或者需要后端人员先实现一些服务功能。这就和刚才提到的“良好的分层结构”相冲突。
每一种技术和框架都有一定的学习曲线。开发人员需要了解具体细节,才知道如何把项目整合成一个完整的解决方案。事实上,一个整合良好的项目框架不仅仅能实现技术、业务的分离,还应该关注并满足开发人员的“隔离”。
为了解决此类问题,便产生了Spring Boot这一全新框架。Spring Boot就是用来简化Spring应用的搭建以及开发过程。该框架致力于实现免XML配置,提供便捷,独立的运行环境,实现“一键运行”满足快速应用开发的需求。
与此同时,一个完整的Web应用难免少不了数据库的支持。利用JDBC的API需要编写复杂重复且冗余的代码。而使用O/RM(例如Hibernate)工具需要基于一些假设和规则,例如最普遍的一个假设就是数据库被恰当的规范了。 这些规范在现实项目中并非能完美实现。由此,诞生了一种混合型解决方案——Mybatis。 Mybatis是一个持久层框架 , 它从各种数据库访问工具中汲取大量优秀的思想,适用于任何大小和用途的数据库。根据官方文档的描述:MyBatis 是支持定制化 SQL、存储过程以及高级映射的优秀的持久层框架。M yBatis 避免了几乎所有的 JDBC 代码和手动设置参数以及获取结果集。MyBatis 可以对配置和原生Map使用简单的 XML 或注解,将接口和 Java 的 POJOs(Plain Old Java Objects,普通的 Java对象)映射成数据库中的记录。
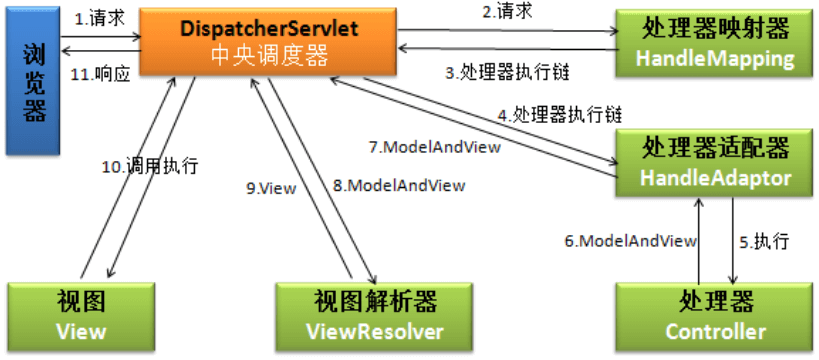
最后,再回到技术结构分层上,目前主流倡导的设计模式为MVC,即模型(model)-视图(view)-控制器(controller)。实现该设计模式的框架有很多,例如Struts。而前文提到的SpringMVC是另一个更为优秀,灵活易用的MVC框架。 SpringMVC是一种基于Java的以请求为驱动类型的轻量级Web框架,其目的是将Web层进行解耦,即使用“请求-响应”模型,从工程结构上实现良好的分层,区分职责,简化Web开发。
目前,对于如何把这些技术整合起来形成一个完整的解决方案,并没有相关的最佳实践。将Spring Boot和Mybatis两者整合使用的资料和案例较少。因此,本文提供(介绍)一个完整利用SpringBoot和Mybatis来构架Web项目的案例。该案例基于SpringMVC架构提供完整且简洁的实现Demo,便于开发人员根据不同需求和业务进行拓展。
补充提示,Spring Boot 推荐采用基于 Java 注解的配置方式,而不是传统的 XML。只需要在主配置 Java 类上添加“@EnableAutoConfiguration”注解就可以启用自动配置。 Spring Boot 的自动配置功能是没有侵入性的,只是作为一种基本的默认实现。开发人员可以通过定义其他 bean 来替代自动配置所提供的功能,例如在配置本案例数据源(DataSource)时,可以体会到该用法。
=====================
首先分析一下各个框架的职责:
SpringMVC:负责表现层
Service接口:处理业务
Mapper:持久层
spring负责将各层之间整合
通过Spring管理持久层的mapper(相当于Dao接口)
通过Spring管理业务层的service,service中可以调用mapper接口
Spring进行事务控制
通过Spring管理表现层handler,handler中可以调用service接口
mapper、service、handler都属于javabean
二、集成MyBatis
Spring Boot 集成MyBatis有两种方式,一种简单的方式就是使用MyBatis官方提供的:
Mybatis 官方提供了 mybatis-spring-boot-starter
https://github.com/mybatis/spring-boot-starter
http://www.mybatis.org/spring-boot-starter/mybatis-spring-boot-autoconfigure/
另外一种方式就是仍然用类似 mybatis-spring
的配置方式,这种方式需要自己写一些代码,但是可以很方便的控制MyBatis的各项配置。
mybatis有很多优点。
- 易于上手和掌握。
- sql写在xml里,便于统一管理和优化。
- 解除sql与程序代码的耦合。
- 提供映射标签,支持对象与数据库的orm字段关系映射
- 提供对象关系映射标签,支持对象关系组建维护
- 提供xml标签,支持编写动态sql。
缺点:笔者自己总结了下(建议使用注解和sql 构建器来写mybatis ,如果使用xml 就会有一些麻烦事了。)
- 其实在开发过程中还是有一些不方便的地方以下列成几种。大多数人习惯于xml 形式。spring loader 不支持热部署xml 的。如果写入sql 构建器。就是通过java 代码来构建sql 又很多人不是特别了解。所以,你改一次就要重启。就有点麻烦了。(笔者最不喜欢就是干浪费时间的事了。)
- 就是mybatis 每次写一个实体的查询语句。就要建立一个mapper 和xml 进行映射。这样Mapper越来越多和xml 越来越多。感觉不好管理,= = !。
三、mybatis-spring-boot-starter方式
1、在 pom.xml
中添加依赖:
需要导入 mybatis-spring-boot-starter
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0</version>
</dependency>
MySQL:
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/mysql/mysql-connector-java -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
mybatis-spring-boot-starter
依赖树如下:

其中 mybatis
使用的3.3.0版本,可以通过:
<mybatis.version>3.3.0</mybatis.version>
属性修改默认版本。
mybatis-spring
使用版本1.2.3,可以通过:
<mybatis-spring.version>1.2.3</mybatis-spring.version>
修改默认版本。
2. 配置文件、application.properties
jdbc.driverClassName = com.mysql.jdbc.Driver jdbc.url = jdbc:mysql://xxx:3306/mytestdb?zeroDateTimeBehavior=convertToNull&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8 jdbc.username = root jdbc.password = vvvxxx mybatis.typeAliasesPackage=com.xxx.firstboot.domain mybatis.mapperLocations=classpath:mapper/*.xml
说明:
- mybatis.typeAliasesPackage:指定domain类的基包,即指定其在*Mapper.xml文件中可以使用简名来代替全类名(看后边的UserMapper.xml介绍)
-
mybatis.mapperLocations:指定*Mapper.xml的位置
除了上面常见的两项配置,还有:
- mybatis.config:mybatis-config.xml配置文件的路径
- mybatis.typeHandlersPackage:扫描typeHandlers的包
- mybatis.checkConfigLocation:检查配置文件是否存在
-
mybatis.executorType:设置执行模式(
SIMPLE, REUSE, BATCH),默认为SIMPLE
3. 代码
主函数:
使用注解方式annotation形式:
【Application.java】包含main函数,像普通java程序启动即可
此外,该类中还包含和数据库相关的DataSource,SqlSeesion配置内容。
注: @MapperScan ( sample.mybatis.mapper ) 表示Mybatis的映射路径(package路径)
@SpringBootApplication @MapperScan("sample.mybatis.mapper") public class Application implements CommandLineRunner { @Autowired private CityMapper cityMapper; public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args); } @Override public void run(String... args) throws Exception { System.out.println(this.cityMapper.findByState("CA")); } }
xml方式:mybatis-config.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"> <configuration> <typeAliases> <package name="sample.mybatis.entity"/> </typeAliases> <mappers> <mapper resource="sample/mybatis/mapper/CityMapper.xml"/> </mappers> </configuration>
application.properties
spring.datasource.schema=import.sql mybatis.config=mybatis-config.xml
定义一个java的实体类:
public class User {
Integer id;
String name;
Integer age;
}
说明:该接口中有两个方法,
- 一个普通插入:直接用 @Mapper 注解搞定
- 一个插入返回主键:需要使用xml来搞定
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select;
/**
* Created by Administrator on 2016/9/2.
*/
@Mapper
public interface UserMapper {
@Select("select * from user where name = #{name}")
User findUserByName(@Param("name")String name);
/**
* 插入用户,并将主键设置到user中
* 注意:返回的是数据库影响条数,即1
*/
public int insertUserWithBackId(User user);
}
xml文件: <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!-- 指定工作空间,要与接口名相同,源代码没有去看,猜测应该是通过"这里的namespace.下边方法的id"来定位方法的 -->
<mapper namespace="com.xxx.firstboot.mapper.UserMapper">
<!-- 若不需要自动返回主键,将useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id"去掉即可(当然如果不需要自动返回主键,直接用注解即可) -->
<insert id="insertUserWithBackId" parameterType="User" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id" >
<![CDATA[
INSERT INTO tb_user
(
username,
password
)
VALUES
(
#{username, jdbcType=VARCHAR},
#{password, jdbcType=VARCHAR}
)
]]>
</insert>
</mapper>
service使用:
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
public class UserService {
@Autowired
UserMapper userMapper;
public String user(){
User user = userMapper.findUserByName("王");
return user.getName()+"-----"+user.getAge();
}
}
四、mybatis-spring方式
这种方式和平常的用法比较接近。需要添加 mybatis
依赖和 mybatis-spring
依赖。
然后创建一个 MyBatisConfig
配置类:
/**
* MyBatis基础配置
*
* @author liuzh
* @since 2015-12-19 10:11
*/
@Configuration
@EnableTransactionManagement
public class MyBatisConfig implements TransactionManagementConfigurer {
@Autowired
DataSource dataSource;
@Bean(name = "sqlSessionFactory")
public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactoryBean() {
SqlSessionFactoryBean bean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
bean.setDataSource(dataSource);
bean.setTypeAliasesPackage("tk.mybatis.springboot.model");
//分页插件
PageHelper pageHelper = new PageHelper();
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.setProperty("reasonable", "true");
properties.setProperty("supportMethodsArguments", "true");
properties.setProperty("returnPageInfo", "check");
properties.setProperty("params", "count=countSql");
pageHelper.setProperties(properties);
//添加插件
bean.setPlugins(new Interceptor[]{pageHelper});
//添加XML目录
ResourcePatternResolver resolver = new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver();
try {
bean.setMapperLocations(resolver.getResources("classpath:mapper/*.xml"));
return bean.getObject();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
@Bean
public SqlSessionTemplate sqlSessionTemplate(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) {
return new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory);
}
@Bean
@Override
public PlatformTransactionManager annotationDrivenTransactionManager() {
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource);
}
}
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
上面代码创建了一个 SqlSessionFactory
和一个 SqlSessionTemplate
,为了支持注解事务,增加了 @EnableTransactionManagement
注解,并且反回了一个 PlatformTransactionManager
Bean。
另外应该注意到这个配置中没有 MapperScannerConfigurer
,如果我们想要扫描MyBatis的Mapper接口,我们就需要配置这个类,这个配置我们需要单独放到一个类中。
/**
* MyBatis扫描接口
*
* @author liuzh
* @since 2015-12-19 14:46
*/
@Configuration
//TODO 注意,由于MapperScannerConfigurer执行的比较早,所以必须有下面的注解
@AutoConfigureAfter(MyBatisConfig.class)
public class MyBatisMapperScannerConfig {
@Bean
public MapperScannerConfigurer mapperScannerConfigurer() {
MapperScannerConfigurer mapperScannerConfigurer = new MapperScannerConfigurer();
mapperScannerConfigurer.setSqlSessionFactoryBeanName("sqlSessionFactory");
mapperScannerConfigurer.setBasePackage("tk.mybatis.springboot.mapper");
return mapperScannerConfigurer;
}
}
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
这个配置一定要注意 @AutoConfigureAfter(MyBatisConfig.class)
,必须有这个配置,否则会有异常。原因就是这个类执行的比较早,由于 sqlSessionFactory
还不存在,后续执行出错。
做好上面配置以后就可以使用MyBatis了。
关于分页插件和通用Mapper集成
分页插件作为插件的例子在上面代码中有。
通用Mapper配置实际就是配置 MapperScannerConfigurer
的时候使用 tk.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer
即可,配置属性使用 Properties
。
四、mybatis
注解批量插入:
@Service @Mapper public interface SynonymMapper { @Select("select * from nlp_chinese_synonym where word1 = #{word1}") public List<SynonymEntity> findWord1(@Param("word1")String word1); @InsertProvider(type = SynonymMapperProvider.class, method = "inserList") public int inserList(List<SynonymEntity> synonymEntityList); public static class SynonymMapperProvider { public String inserList(Map<String, List<SynonymEntity>> entity) { List<SynonymEntity> list = entity.get("list"); StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder(256); stringBuilder.append("insert into nlp_chinese_synonym (word1,word2,value,ctime) values"); MessageFormat messageFormat = new MessageFormat("(#'{'list[{0}].word1},#'{'list[{0}].word2},#'{'list[{0}].value},#'{'list[{0}].ctime})"); for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) { stringBuilder.append(messageFormat.format(new Integer[]{i})); stringBuilder.append(","); } stringBuilder.setLength(stringBuilder.length() - 1); stringBuilder.append(" ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE value =value,ctime=ctime"); return stringBuilder.toString(); } } }